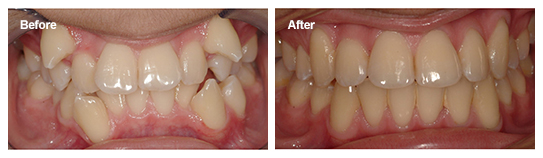
What Is An Impacted Tooth?
April 4th, 2018
FOR MOST PEOPLE, baby teeth become loose and adult teeth erupt in their place. For many, those adult teeth don’t come in entirely straight, so orthodontic treatment is necessary to shift them into the ideal position. For some, one or more of these teeth never emerge on their own, even though they developed in the jaw bone. These are impacted teeth.
Why Does Tooth Impaction Happen?
Tooth impaction is often the result of a crowding problem. If the new tooth doesn’t have room to come in, it may remain stuck beneath the gums. A full impaction is when the tooth fails to erupt at all, whereas a partial impaction is when the tooth breaches the gumline but doesn’t grow in completely.
Teeth Lost In The Gums
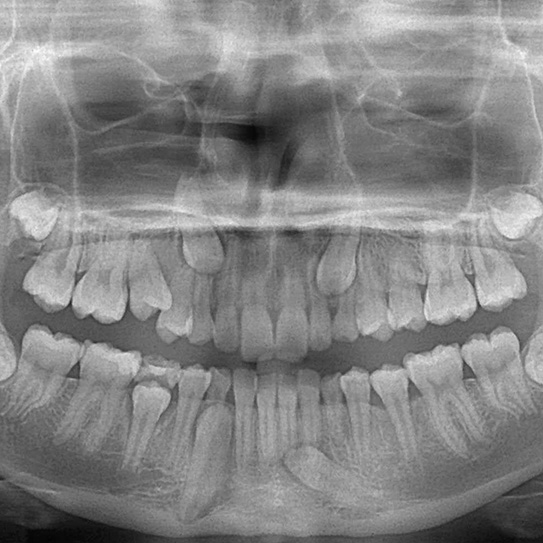
The most common teeth to become impacted are wisdom teeth. They might be impacted because there isn’t room for them in the jaw, they may be crooked, or they could even be completely sideways, threatening the roots of second molars. Another tooth commonly impacted is the upper maxillary canine, and lower mandibular canines and upper and lower premolars can be impacted as well.
Research shows that if there’s a history of impacted upper canines in your family, you are more likely to have them as well. Most often, only one canine will be impacted, but sometimes both are. Why the upper canines? Normally, they come in after the incisors and the premolars. When those don’t leave enough room between them, the canines have nowhere to go.
Symptoms And Complications Of Impacted Teeth
Some people with an impacted tooth show no symptoms except that the tooth doesn’t erupt. If it’s a canine, the baby tooth may not even loosen on its own! But even without symptoms, canine teeth are critical to a great smile because they provide essential structure and support. They also take on much of the chewing pressure thanks to their longer roots, which protects the surrounding teeth.
Impacted teeth often cause complications and symptoms besides a lopsided smile. Impacted teeth can push into neighboring teeth beneath the gums and cause cavities, infections, gum disease, or nerve damage. Symptoms might include bad breath, pain, tenderness around the jawline, a prolonged headache or jaw ache, swollen gums, swollen lymph nodes, bad taste in mouth, and visible gaps.
Treatment: A Place For Every Tooth
Impaction of a tooth usually can’t be prevented, but the tooth can be removed (in the case of wisdom teeth) or moved into its proper position (in the case of canines) with oral surgery and orthodontic treatment. An impacted tooth is usually discovered through dental x-rays, and then the orthodontist can determine the best course of action to take.